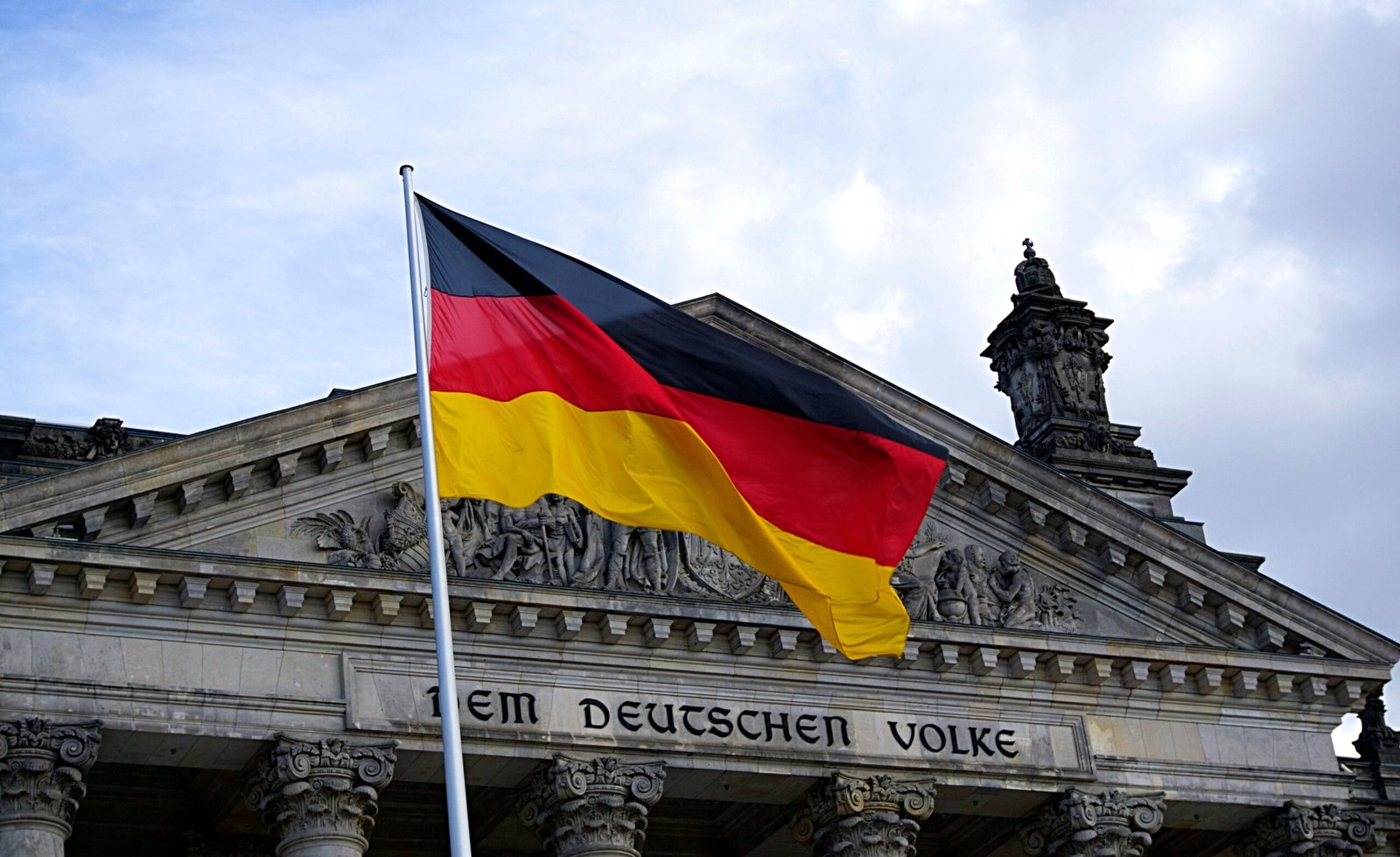
Study in Germany
Germany is one of the most renowned non-English-speaking countries in the world, celebrated for its automobiles, sausages, beer, bread, castles, cathedrals, and football. However, what truly draws students from across the globe is its tuition-free or low-cost education, making it a top destination for aspiring international students. Germany’s reputation for academic excellence has led to a significant increase in international student enrollment, with nearly 400,000 students currently pursuing higher education in the country. Students come from diverse nations including China, India, Russia, Austria, Italy, France, the UK, Ukraine, Turkey, and Bulgaria. This multicultural environment enhances both academic and cultural experiences.
Over the past few years, Germany has solidified its status as one of the most popular destinations for international students seeking high-quality education and global career opportunities. If you are considering studying in Germany, it's essential to start by choosing a university and program that aligns with your academic interests and career goals. For personalized guidance and accurate information, it is highly recommended to connect with professional Germany education consultants. To understand the application process, eligibility requirements, and how to begin your study abroad journey in Germany, reach out to the experienced advisors at MasterKey Solutions — your trusted partner in global education.

Education System for Study in Germany for Indian Students
Germany offers two main types of higher education institutions: public and private universities. What may come as a pleasant surprise to many is that public universities in Germany do not charge tuition fees, making them an attractive option for international students. In contrast, private universities can be relatively expensive.
There are approximately 400 public universities and 120 private universities across Germany. Many of these institutions embrace the concept of "academic freedom," allowing students the flexibility to study at their own pace without the pressure of mandatory class attendance.
If you're looking to pursue a high-quality education at a low cost while enjoying a more flexible and stress-free academic lifestyle, Germany is an ideal destination. A qualified education advisor can help you identify the most affordable and suitable options for studying abroad.
In terms of academic structure:

Types of Intakes: Study in Germany
Germany offers two major study abroad intakes each year, giving students the flexibility to choose the one that best aligns with their academic goals and personal preferences. These dual intakes help manage student volume, as accommodating all applicants in a single intake would be challenging.
The Winter Intake generally sees larger class sizes and is considered more popular. Many professors commence their research projects during the winter term, leading to increased opportunities for employment, assistantships, and academic collaboration. Additionally, extracurricular activities and campus events are more frequent during this period, enriching the overall student experience.
That said, some programs may be offered only during the Summer Intake. So, regardless of the season, if your preferred course is available, don’t delay—submit your application as early as possible to secure a spot. And remember, visa approval is essential for any intake, so be sure to plan ahead and prepare all necessary documentation in time.
Research Universities 97%
Technical Universities 96%
Colleges of Art, Film & Music 98%
Universities of Applied Sciences 99%





1. Medicine and Dentistry
2. Law
3. Mathematics and Computer Science
4. Natural Sciences (Pure Sciences)
5. Business and Economics
6. Architecture
7. International Literatures Masters
8. Psychology
9. Earth Sciences
10. English Literatures and Cultures Masters
11. Languages, History and Cultures of The Middle East Masters
12. Egyptology Masters
13. Empirical Cultural Studies Masters
14. Literary Theory Masters
Germany has seen a significant rise in international student applications due to its evolving industry, excellent education system, and affordable tuition fees (many universities charge under €1,000/year).
Key Admission Requirements & Steps:
1. Entrance Exams: Depending on the course, tests like TOEFL, IELTS, GRE, GMAT, SAT, or ACT may be required.
2. Academic Qualification: A school-leaving certificate or equivalent is necessary. If your education doesn't meet the criteria, a foundation course may be required.
3. Financial Proof: You must show evidence of funds—around €8,700 plus tuition fees if applicable.
4. DAAD Website: Use the DAAD portal to check if your qualifications are valid for German university admissions.
5. Anabin Database: Check Anabin.de to verify if your institution is recognized in Germany (use Google Translate if needed).
6. Aptitude Test: Some programs require Test AS (approx. €80), testing language, cognitive, and subject knowledge.
7. Language Skills: While not always mandatory, learning basic German is helpful. Ensure your chosen course is taught in English if needed.
In 2014, tuition fees were abolished in 16 German states for both domestic and international students, making Germany one of the most affordable study destinations in Europe. However, it’s important to note that the Federal State of Baden-Württemberg still charges a tuition fee of approximately €1,500 per semester for non-EU international students. Many universities across Germany continue to offer low or no tuition fees, significantly reducing the financial burden on international students. If you’d like a detailed breakdown of the total cost of studying in Germany, including tuition, living expenses, and additional fees, we recommend speaking with our expert Germany education consultants for accurate and personalized guidance.
While tuition fees are low or non-existent at most public universities in Germany, almost all universities charge a semester contribution, typically around €250 per semester. This fee often covers student services, public transportation, and other campus facilities. Additionally, most institutions charge an administrative fee of approximately €50 per semester. For living expenses, international students should budget around €850 per month, which covers accommodation, food, health insurance, and other daily necessities.
When you study in Germany, students are entitled to various concessions and discounts by simply presenting their student ID card—similar to the benefits available in the UK. These discounts often apply to public transport, museums, cinemas, and more. The biggest monthly expense for most students is accommodation, which typically ranges between €210 and €350 depending on the city and type of housing. Additionally, health insurance costs around €80 per month. Altogether, a student should expect to spend a little over €800 per month to cover living expenses. For a detailed cost breakdown and personalized budgeting advice, consult our expert Germany education consultants.
Our power of choice is untrammelled and when nothing prevents being able to do what we like best every pleasure.
Germany is renowned for its tuition-free education system, but it’s important to note that visa regulations and university application procedures can be more stringent compared to other countries. To study in Germany, international students must apply for a student visa, which typically costs around €60. It is highly recommended to apply at least three months in advance of your intended travel date to allow ample time for processing. Our experienced Germany education consultants are here to support you throughout the entire journey—including guidance on visa documentation, application submission, and interview preparation—to ensure a smooth transition to studying abroad in Germany.
-> Proof of sufficient funds to support oneself in Germany for a year (about 8700 pounds per month plus university fees).
-> Academic transcripts, proficiency in either German or English, depending on the language of the course.
-> Authentication of all documents required
-> Health insurance certificate (80 euros per month)
-> A copy of your criminal record must be provided.
-> A well-filled out application
-> Two recent photographs
-> Letter of acceptance from the university
After graduation, international students holding a valid residence permit are generally allowed to stay and work in Germany for up to 18 months, particularly if employed in a field related to their studies. Meanwhile, graduates from EU and EEA countries face no such restrictions and are free to pursue employment opportunities. If you’ve worked in Germany for around two years, you may become eligible to apply for permanent residency. While speaking German is not mandatory, it can significantly enhance your job prospects and integration into the workplace. For expert guidance on post-study work options, visa extensions, and residency pathways, connect with MasterKey Solutions top Germany education consultants.
-> GyanDhan Scholarship
-> DAAD Scholarship Programs
-> Heinrich Böll Foundation Scholarships
-> DeutschlandStipendium National Scholarship Programme
-> Konrad-Adenauer-Stiftung Scholarships in Germany for International Students
International students with a German student visa can work up to 120 full days or 240 half-days per year, but actual work limits may vary based on location, job type, and other factors. It’s important to understand these rules to stay compliant. For personalized guidance, consult expert Germany education consultants.
You must adhere to the following basic rules:
@ If you plan to work in Germany, you must obtain a work permit from the Alien Registration Office (Agentur für Arbeit) and relevant financial authorities. The permit will specify the maximum number of working hours allowed. Typically, students are permitted to work up to 20 hours per week during academic terms and full-time during vacation periods. Please note, if you are a non-EU student, different rules and restrictions may apply.
@ The minimum wage is approximately 8.84 euros per hour (an increase was made in 2017).
@ There may be fewer regulations if you are enrolled in a preparatory or language course. Furthermore, you will need explicit permission to work in such circumstances.
@ If you have worked less than 5.50 consecutive days during a one-year period, you are not required to pay tax.
@ Income tax is not imposed on individuals earning less than 450 euros per month. Despite this, some research assistants are exempt from paying taxes.
@ It is recommended that students don’t work more than 20 hours per week, not because it is illegal, but because it will increase the cost of certain expenses.
@ An internship on a university campus can be of considerable benefit to a student. Most often, longer working hours are permitted, and taxes may also be exempt.
Work as a waiter, server, support member, etc., at bars, cafes. | English Tutor. If you’re perfect at the language. | Graduate / Research / Teaching Assistant | Internship related to your field, etc.
Germany is renowned worldwide for its strong automobile industry, making a degree in automobile engineering or related fields highly valuable. Besides automotive, industries such as telecommunications, IT and computing, and finance are also thriving. International students planning to study in Germany can explore a wide range of job opportunities across these growing sectors, offering excellent career prospects.
- Is there a minimum IELTS score required to study in Germany?
-
For certain technical courses in Germany, a minimum IELTS score of 6.5 is required. Additionally, you can send your IELTS score to up to five universities within one month of taking the exam.
- Are there any degree programs in Germany that are taught in English?
-
Yes, you can study in Germany in English, as many international degree programs are offered entirely in English. These programs are specifically designed for international students who may not have sufficient proficiency in German to enroll in courses taught in German. By searching for “international study programs in Germany,” you’ll find a wide range of English-language options to pursue your studies abroad.
- Can a student bring their family members on a student visa?
-
During their studies, international students may be allowed to bring their parents to stay with them in Germany, subject to certain conditions. For detailed information and assistance, please contact our Germany education consultants.
- Does Germany require health insurance for students?
-
Yes, health insurance is mandatory for studying abroad in Germany. International students are eligible to join the public health insurance system (statutory health insurance). Specifically, degree students under the age of 30 can register with a public health insurance provider instead of opting for private insurance.
- Is it difficult to learn German, since it is the local and most commonly spoken language?
-
A common misconception among international students is that German is a difficult language to learn. In reality, it is often easier to pick up than many people think.
- What is the best way to travel around Germany without a personal vehicle?
-
If you don’t have a personal vehicle, getting around Germany is still very convenient. The country boasts a comprehensive and efficient public transportation system. This includes buses, trains, suburban commuter rails (S-Bahn), as well as subways and underground trains (U-Bahn).
- Is there a scholarship program available to cover the expenses of students?
-
International students studying in Germany have access to a variety of scholarships. These include government-sponsored scholarships like the DAAD Scholarship and Erasmus+, as well as non-government scholarships and those offered directly by German universities.
- For English-taught courses, is it necessary to pass TOEFL or IELTS?
-
If you are a native English speaker, you are not required to submit TOEFL or IELTS scores. However, to apply for a fully English-taught program at a German university, non-native speakers must provide TOEFL or IELTS scores. Additionally, if you are applying for a postgraduate program and already hold an undergraduate degree from an English-taught course, you typically do not need to take these tests.
 Demos
Demos  Colors
Colors 
 Docs
Docs  Support
Support